What are biogenic amines and why can they be an issue?
By Deborah Parker Wong
Most knowledgeable wine customers have accepted the truth that sulfur isn’t the foundation reason for wine complications, however the false impression that sulfur dioxide (SO2) causes adversarial reactions to wine consumption remains to be usually perpetuated by the media and might persist amongst informal customers. As a substitute, what’s been recognized as a supply of adversarial reactions to no- and low-sulfur crimson wines, significantly by histamine-sensitive customers, are biogenic amines (BA).
The Fundamentals
Biogenic amines in wine are a byproduct of fermentation and malolactic conversion. They’re natural compounds produced by yeasts and lactic acid micro organism throughout a course of that reduces the carboxyl group in amino acids and raises the pH, making a extra hospitable setting for the expansion and survival of the lactic acid micro organism.
In consequence, a number of totally different amines are produced, with tyramine and histamine being essentially the most frequent and problematic. Collectively, they will trigger a synergistic response referred to as “biogenic amine toxicity,” which is characterised by complications, migraine, nausea, vomiting and hypertension. Sulfite reactions, alternatively, are nearly solely restricted to respiratory signs affecting victims of acute bronchial asthma.
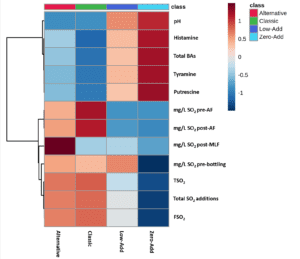
Curiously, some no- and low-sulfur wines comprise elevated BA ranges, whereas others comprise none. In cellars the place biogenic amine ranges are excessive, a mixture of upper pH musts, native ferments, and no- or low-sulfur additions on the finish of malolactic conversion are the important thing contributing elements. The ensuing wines let lactic acid micro organism stay metabolically lively, which results in rising quantities of amines produced throughout getting old.
To stop BA from forming, winemakers can inoculate for malolactic conversion, guarantee pH ranges stay low, and use SO2 to maintain microbial load to a minimal.
The Examine
In a paper titled “What Is the Relationship Between the Use of Sulphur Dioxide and Biogenic Amine Ranges in Wine?,” Sophie Parker Thompson, MW, notes that the results of biogenic amines in wine are heightened as a result of ethanol and acetaldehyde, compounds that happen naturally in wine and inhibit our physique’s capability to detoxify these results, making a compelling argument for establishing a low-BA class of wine.
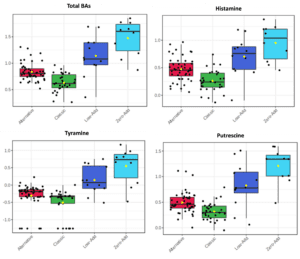
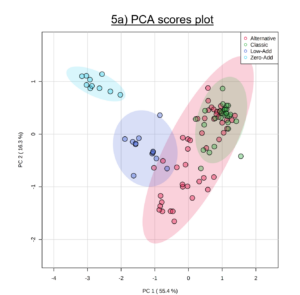
Her examine of 100 New Zealand Sauvignon Blancs included a cross-section of wine kinds and sulfur dioxide regimes: traditional, various, low- and zero-SO2 wines. Evaluation for 3 biogenic amines — histamine, tyramine and putrescine — revealed very excessive biogenic amine concentrations in zero- and low-SO2 wines, whereas the bottom concentrations had been recorded within the traditional wine type with whole SO2 additions of higher than 65 to 80 mg/L.
From a sensory perspective, essentially the most prolific biogenic amine-producing micro organism are additionally the reason for wine faults, together with mousiness (which some customers usually are not genetically capable of detect) and ropiness. In response to Parker Thompson, “It’s past coincidence that signs of biogenic amine toxicity mirror the anecdotal proof for adversarial reactions from wine consumption.”
The Testing
In winemaking, there are three key stipulations for elevated ranges of BA manufacturing: availability of free amino acids or proteins, microbes with decarboxylase genes, and situations that favor microbial development.
Casey Graybehl, R&D winemaker and manufacturing director for Obsidian Wine Co. in Sonoma, Calif., makes three glorious high quality, low-sulfur wines for the corporate’s Rabbit Gap label: Máslás, a piquette; Pezsgö, petillant naturel; and Pear Blanc, a glowing grape and pear wine. Graybehl was interested in amine manufacturing and had the 2021 vintages examined.
“Our winemaking practices for the Rabbit Gap wines, that are sometimes bottled instantly after harvest, embrace native yeasts, low pH musts with solely a small quantity of sulfur added pre-bottling to inhibit malolactic fermentation, and 0 filtration or fining. Whereas this would appear like a state of affairs for biogenic amines to be produced, upon testing we didn’t see elevated ranges over our extra commonplace winemaking practices. It’s very possible that our low pH musts are inhibiting amine manufacturing.”
If BA ranges are excessive in a wine, it may be handled with a extremely acidic, silica-based additive to take away biogenic amines. Impacts of therapy can embrace an preliminary lower in ethyl esters (that recovered after a number of days), and a perceptible impression on wine shade (in all probability as a result of a slight lower within the pH of handled wines). The proposed method could be higher suited to wines aged in barrels than for younger wines.
The Actuality
Loved alone, wines with regular ranges of biogenic amines aren’t more likely to set off a response. However delicate customers who unwittingly pair wines which have elevated BA ranges with meals (together with aged cheese and charcuterie) which can be wealthy in amines are at far higher threat for adversarial reactions; alcohol and a few drugs, together with statins, additionally improve BA’s poisonous impact. Research have proven {that a} mere 10 mg of tyramine can set off the onset of migraine and, in meals with totally different ranges of histamine, signs of biogenic amine toxicity occurred “at ranges between 75 mg to 300 mg” in each histamine-intolerant and wholesome customers.
As a result of consumption of biogenic amines can pose a risk to human well being, the Meals and Drug Administration has set a authorized restrict of fifty ppm (5 mg/100 g) of histamine in seafood merchandise, however no particular rules exist for biogenic amines in different meals stuffs — or for histamines in wine.
The outcomes of Parker Thompson’s examine display that sulfur is a crucial, if not an important, think about avoiding poisonous biogenic amine ranges in wine, which is in direct battle with the present tendencies in no- or low-sulfur dioxide wines. She concludes, “If SO2 additions are unconscionable for the Pure Wine motion, maybe zero-added SO2 wines ought to carry a compulsory high-BA warning — until they will show in any other case.”
_______________________________________________________
 Deborah Parker Wong
Deborah Parker Wong
Deborah Parker Wong, DipWSET, was appointed nationwide editor, USA for the Gradual Meals Gradual Wine Information in 2020. As international wine editor for sister publications the SOMM Journal and The Tasting Panel magazines, she has been writing concerning the beverage alcohol trade for these and different shops since 2004. She teaches as an adjunct professor within the Wine Research departments at Santa Rosa Junior School and Cabrillo School and owns a Wine & Spirit Schooling Belief college providing Stage 2 and Stage 3 certifications. Along with writing and talking about wine, she is presently pursuing a Grasp’s Diploma in Viticulture and Enology at California State College, Fresno. www.deborahparkerwong.com



