Sugars play a key half within the brewing course of and in case you are accustomed to the fundamentals of fermentation you’ll know yeasts want sugars for the gasoline to maintain them working effectively. As they ferment the sugars within the wort they convert them into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
Low alcohol beers or alcohol free beers will typically comprise as much as 28 g of sugar because it has not been transformed into alcohol by the yeast or “fermented” as such.
Many of the sugars used come from starches within the grain that are damaged down because the grains are malted, however not all sugars within the grains are fermentable, and understanding the position of non-fermentable sugars in brewing is essential for attaining the specified taste and texture within the remaining product.
You might also need to add sugars to the brew, particularly if brewing onerous cider, to sweeten the drink or give it a lighter physique with out the completed brew being like rocket gasoline in energy.
What precisely are fermentable and non-fermentable sugars? What are the important thing variations and what are the very best non-fermentable sugars to make use of in brewing?
What are Non-fermentable Sugars?

Non-fermentable sugars are mainly sugars that can not be transformed into alcohol through the brewing course of. A non-fermentable sugar, whereas it won’t contribute to the alcohol ranges (ABV) of the beer, can contribute to the general taste and mouthfeel of a beer.
Non-fermentable sugars play an essential position within the brewing course of, and controlling their ranges is essential to producing top quality beer.
These sugars are usually extra advanced and embrace dextrins, that are massive, unfermentable sugar molecules. They’re created when the enzymes within the mash can not break down the starches within the grains into smaller, fermentable sugars.
In the course of the brewing course of, the mash is heated to activate the enzymes within the grain, which convert the starches into easier sugars that yeast can ferment. Nonetheless, if the temperature is just too excessive or the mash is just not blended nicely sufficient, a few of the starches won’t be absolutely transformed, leading to non-fermentable sugars within the remaining product.
One of many main forms of non-fermentable sugars in brewing are dextrins, accountable for a few of the sweetness in beer and helpful for balancing the bitterness from the hops.
The extent of non-fermentable sugars in beer is influenced by quite a lot of components, together with the forms of grains used, the mash temperature, and the size of the brewing course of. Usually, darker malts and grains comprise extra non-fermentable sugars than lighter malts, leading to a thicker, creamier beer.
Brewers can management the extent of non-fermentable sugars by rigorously controlling the mash temperature, which impacts the exercise of the enzymes that break down the starches within the grains.
If the mash temperature is just too excessive, the enzymes might denature, leading to incomplete starch conversion and better ranges of non-fermentable sugars within the remaining product.
Whereas non-fermentable sugars are important for attaining the specified taste and mouthfeel in beer, too many of those sugars also can negatively influence the ultimate product. Excessive ranges of non-fermentable sugars may end up in a beer that’s overly candy and has a cloying mouthfeel.
Moreover, non-fermentable sugars may cause issues through the brewing course of, similar to low alcohol content material and poor fermentation.
The upper the quantity of non-fermentable sugars, the extra full-bodied and creamy the beer might be.
What’s the Distinction Between Fermentable and Non-fermentable Sugars?
In the course of the brewing course of, fermentable sugars are transformed by yeast and different microorganisms into alcohol and carbon dioxide via a course of referred to as fermentation. This course of is what provides beer its attribute taste and carbonation.
The quantity of fermentable sugars utilized in a recipe can influence the ultimate alcohol content material of the beer, in addition to its stage of sweetness, dryness, and different taste traits.
The fermentable sugars are glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose, and maltotriose, and customarily account for 60%–70% of the full dissolved solids within the wort. Mashing circumstances that favor the motion of the enzymes beta amylase and restrict dextrinase within the mash create extra fermentable worts. Easy sugars could be added to the wort to extend its fermentability.
Fermentable sugars are classed as together with oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols. They’re composed of quick chains of sugar molecules, making them straightforward to interrupt down.
Dextrins, by comparability, are polysacherides which have 10 or extra sugar molecules joined collectively in a sequence. Yeasts don’t produce sufficient of the enzymes to interrupt down the chains of a dextrin and subsequently they aren’t fermented or transformed in CO2 and alcohol.
Consider it as a steak. When a steak is minimize into smaller items by your enamel or with a knife and fork, it’s simpler for the human physique to digest. Sadly, yeast doesn’t have any enamel or knives and forks, simply enzymes which might break down the sugars.
And, much more sadly, yeast doesn’t have the required enzymes to interrupt down the dextrins, so they continue to be largely unfermented and don’t give any further taste to the beer (though the undissolved sugars could make a beer sweeter) however can change the physique of the beer, making it lighter in some circumstances.
The Molecular make-up of a Dextrin
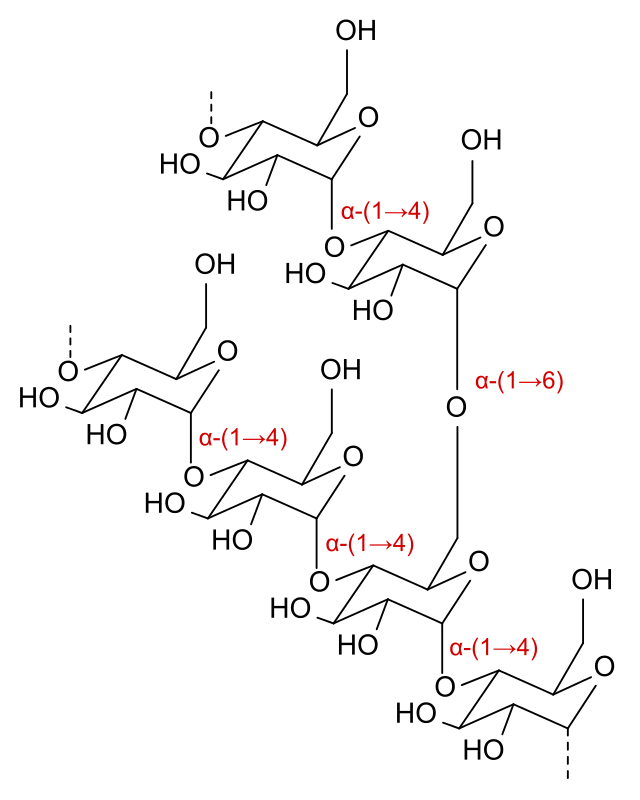
Non-fermentable sugars don’t contribute to the manufacturing of alcohol or carbon dioxide throughout fermentation. As a substitute, they will influence the physique, mouthfeel, and sweetness of the beer. Lactose, one other non-fermentable sugar, is usually utilized in stouts and porters so as to add sweetness and enhance the physique of the beer with out impacting the alcohol content material.
Some kinds of beer, similar to stouts and porters, rely closely on non-fermentable sugars for his or her signature flavors and textures. These beers are usually made with darkish roasted malts that comprise extra non-fermentable sugars than lighter malts, leading to a thicker, creamier beer.
To attain the right stability of fermentable and non-fermentable sugars, brewers should rigorously management the mash temperature, combine the grains totally, and use the appropriate mixture of malts. They might additionally use completely different strains of yeast that may higher ferment sure forms of sugars, or add enzymes to interrupt down the advanced sugars into easier, fermentable ones.
For instance, some yeast strains are higher at fermenting dextrins than others. Brewers may add enzymes to interrupt down the advanced sugars into easier, fermentable ones, or they might use a mixture of malts that comprise each fermentable and non-fermentable sugars.
Ought to You Add Fermentable Sugars or Non-fermentable Sugars After Fermentation?
It will depend on what you need the sugar to do. For affecting the style or sweetness of the completed beer it’s best to contemplate including a non-fermentable sugar or synthetic sweetener.
After fermentation is accomplished, many brewers will add some fermentable sugar to assist prime and carbonate the beer through a secondary fermentation. The quantity added is so little that it shouldn’t actually produce an excessive amount of extra alcohol, simply sufficient C02 to offer the beer that important fizz.
What Are the Finest Non-fermentable Sugars for Beer?
One of the best non-fermentable sugars for beer depend upon the type of beer and the specified taste and mouthfeel. Nonetheless, there are some generally used non-fermentable sugars which can be standard amongst brewers.
Dextrins are the most typical non-fermentable sugar utilized in brewing. They contribute to the physique and mouthfeel of beer and are accountable for a few of the sweetness.
Dextrins are created when enzymes within the mash can not break down the starches within the grains into easier, fermentable sugars. Darker malts and grains comprise extra dextrins than lighter malts, leading to a thicker, creamier beer.
A generally used non-fermentable sugar in brewing is maltodextrin. Maltodextrin is a fancy carbohydrate made out of corn, rice, or potato starch. It’s typically utilized in brewing to extend the physique and mouthfeel of beer with out including sweetness or altering the flavour.
Maltodextrin is especially helpful in light-bodied beers, similar to lagers, the place a skinny mouthfeel can detract from the general consuming expertise.
Along with dextrins and maltodextrin, different non-fermentable sugars which can be generally utilized in brewing embrace lactose, glycerin, and xylitol. Lactose is a milk sugar that’s generally utilized in stouts and porters so as to add sweetness and enhance the physique of the beer.
Glycerin is a thick, candy liquid that may be added to beer to extend the physique and mouthfeel. Xylitol is a sugar alcohol that’s generally utilized in brewing so as to add sweetness with out contributing to the alcohol content material of the beer.
Finally, the very best non-fermentable sugar for beer will depend on the specified taste and mouthfeel. Brewers can experiment with various kinds of non-fermentable sugars to realize the specified end result, however it’s important to rigorously management the extent of non-fermentable sugars to keep away from over-sweetness or different points that may influence the ultimate product.
Is Monk Fruit a Non-fermentable Sugar?
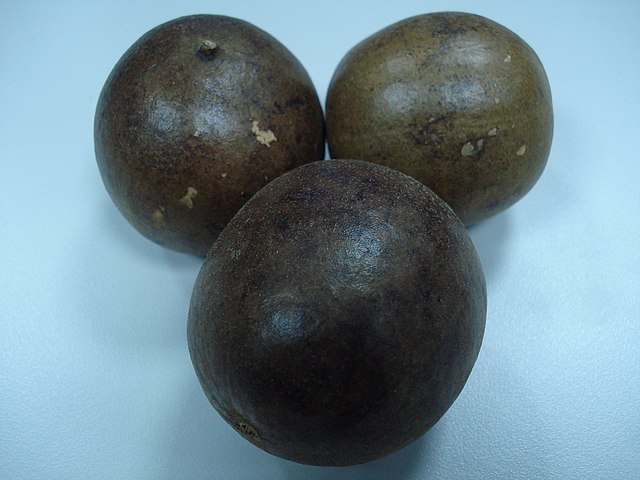

Monk fruit sweetener is a pure sweetener extracted from the fruit of the monk fruit plant, which is native to southern China. The sweetness in monk fruit comes from compounds referred to as mogrosides, that are extracted from the fruit utilizing a water-based course of.
Dogfish head not too long ago launched a low-cal IPA, Barely Mighty utilizing Monk fruit extract for a low carb, low-cal beer which they boast doesn’t style like “seltzer water”.
Whereas mogrosides themselves usually are not fermentable, they’re typically blended with different fermentable sugars similar to erythritol or dextrose to create a low-calorie sweetener that can be utilized as a sugar substitute in brewing. Nonetheless, since these added sugars are fermentable, utilizing monk fruit sweetener as a sugar substitute in brewing might influence the ultimate product’s fermentation and alcohol content material.
In abstract, whereas monk fruit itself is a non-fermentable sugar, its use as a sugar substitute in brewing might influence the ultimate product’s fermentability and alcohol content material if mixed with different fermentable sugars. Brewers ought to rigorously contemplate the influence of utilizing monk fruit sweetener of their recipes and alter their brewing course of accordingly.
Non-fermentable Sugars – Ultimate Ideas
Finally, non-fermentable sugars are a significant element of brewing that contributes to the physique, mouthfeel, and taste of beer. Understanding their position and find out how to management their ranges is essential for producing high-quality beer that showcases the distinctive traits of those advanced sugars.
By rigorously controlling the brewing course of and utilizing the appropriate mixture of malts, brewers can create a spread of scrumptious beers that spotlight the distinctive flavors and textures of non-fermentable sugars.


